https://leetcode.com/problems/populating-next-right-pointers-in-each-node/
Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node - LeetCode
Level up your coding skills and quickly land a job. This is the best place to expand your knowledge and get prepared for your next interview.
leetcode.com
문제
You are given a perfect binary tree where all leaves are on the same level, and every parent has two children. The binary tree has the following definition:
struct Node {
int val;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node *next;
}
Populate each next pointer to point to its next right node. If there is no next right node, the next pointer should be set to NULL.
Initially, all next pointers are set to NULL.
예시
Example 1:
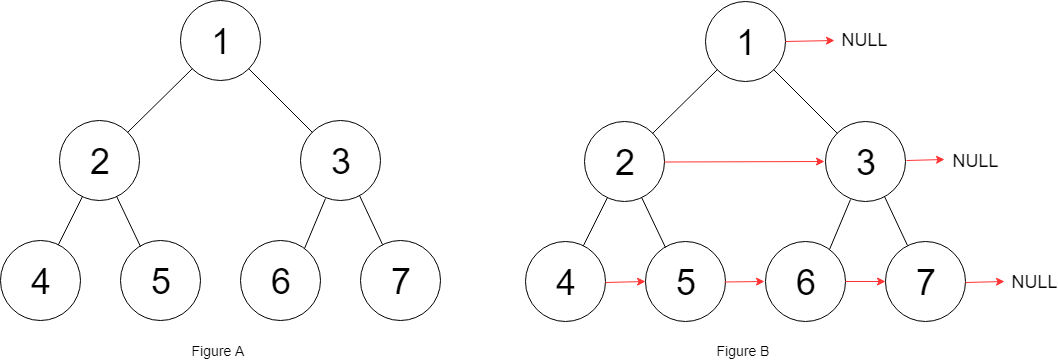
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
Output: [1,#,2,3,#,4,5,6,7,#]
Explanation: Given the above perfect binary tree (Figure A), your function should populate each next pointer to point to its next right node, just like in Figure B. The serialized output is in level order as connected by the next pointers, with '#' signifying the end of each level.
Example 2:
Input: root = []
Output: []
제약 조건
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [0, 212 - 1].
- -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
Follow-up:
- You may only use constant extra space.
- The recursive approach is fine. You may assume implicit stack space does not count as extra space for this problem.
해결 과정
- bfs 순회를 진행하기 위해 노드를 담을 queue 를 준비한다. (첫번째 노드를 미리 세팅한다. [[0, root]])
- queue 의 원소 형태는 [해당노드의 레벨, 해당노드의 값] 형태로 저장해 놓는다.
- queue 가 비워질 때까지 bfs를 진행한다.
- 매 순회마다 아래와 같은 로직으로 현재노드의 다음노드를 지정한다.
- 만약 queue 에 현재 노드를 shift 해왔는데 이외에 다른 노드가 있다면 (if (queue.length)) 이 노드를 다음 노드를 칭하여 함께 shift 해온다.
- 현재노드의 레벨과 다음 노드의 레벨이 같다면 현재 노드의 next 를 다음 노드로 설정하고 레벨이 다르다면 현재 노드의 next 를 null 로 설정한다. 그리고 다음 노드를 다시 queue에 unshift 하여 맨 앞에 복원시킨다.
- 만약 queue 에 현재노드만 존재한다면 다음 노드가 없는것으로 간주하여 현재 노드의 next 를 null로 설정한다.
- crrNode.left와 right값이 있다면 queue에 push를 한 뒤 반복문을 수행한다.
해결 코드
/**
* // Definition for a Node.
* function Node(val, left, right, next) {
* this.val = val === undefined ? null : val;
* this.left = left === undefined ? null : left;
* this.right = right === undefined ? null : right;
* this.next = next === undefined ? null : next;
* };
*/
/**
* @param {Node} root
* @return {Node}
*/
let connect = function(root) {
if (!root) return root;
const queue = [[0, root]];
while (queue.length) {
const [curNodelev, currNode] = queue.shift();
if (queue.length) {
const [nextNodelev, nextNode] = queue.shift();
currNode.next = curNodelev === nextNodelev ? nextNode : null;
queue.unshift([nextNodelev, nextNode]);
} else {
currNode.next = null;
}
currNode.left && queue.push([curNodelev + 1, currNode.left]);
currNode.right && queue.push([curNodelev + 1, currNode.right]);
}
return root;
};
참고 사이트
https://velog.io/@younoah/leetcode-116
[bfs] 116. Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node
leetcode 116. Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node
velog.io
'leetCode' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Medium] 77. Combinations (0) | 2022.05.19 |
|---|---|
| [Easy] 21. Merge Two Sorted Lists (0) | 2022.05.18 |
| [Easy] 206. Reverse Linked List (2) | 2022.05.18 |
| [Medium] 542. 01 Matrix (0) | 2022.05.17 |
| [Easy] 617. Merge Two Binary Trees (0) | 2022.05.16 |

Comment